Synthesis methods and superconducting properties of Nb-Ti alloys
Dispersion oxide strengthening (ODS) is an innovative synthesis method of functional materials with unique properties. They are characterized by excellent mechanical parameters, high thermal and chemical stability, as well as good resistance to ionizing radiation.
A few years ago researchers from the Oxford University proposed using the concept of ODS to prepare a Nb-Ti superconductor with 5% addition of Y2O3. The obtained material was characterized by better superconductive parameters than pure Nb-Ti alloy.
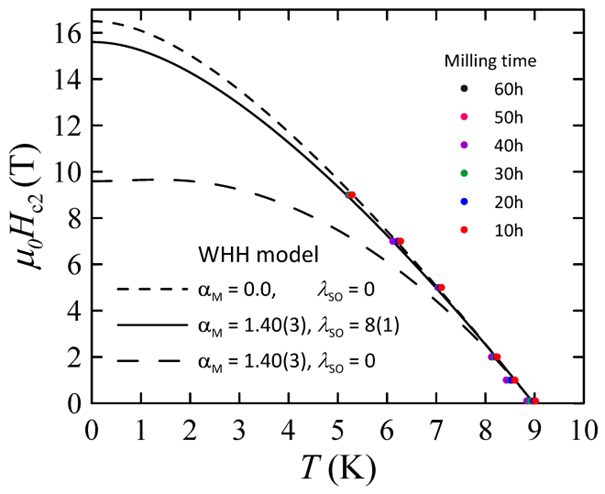
The figure shows the upper critical field as a function of temperature determined for the superconducting Nb-Ti + ZrO2 alloy, which was prepared by planetary mechanical synthesis of Nb-Ti alloy powder and ZrO2 microparticles. The continuous and dashed lines are the simulated WHH curves.
In the recently published work Effect of Dispersed ZrO2 Particles on Microstructure Evolution and Superconducting Properties of Nb-Ti Alloy, Materials 17 (2024) 5946 by Rafał Idczak, Robert Konieczny, Wojciech Nowak, Wojciech Bartz, and Michał Babij, the authors describe ways of synthesis and superconductive properties of Nb-Ti alloys into the volume of which extremely stable zirconium oxide (ZrO2) particles were introduced. Syntheses of this material were done in three various ways using the methods of mechanical sintering and melting in an arc furnace.
The obtained results show that the optimal method of preparation is by planetary mechanical synthesis of Nb-Ti alloy powder and ZrO2 microparticles. The material obtained in this way was characterized by similar critical temperature and higher upper critical field than pure Nb-Ti alloy, as presented in the attached figure.
